Imagine a forest so fragmented that its inhabitants are isolated, unable to navigate their landscape or access essential resources. For howler monkeys, these disruptions extend beyond immediate survival challenges—they erode genetic diversity, threaten population stability, and impair the critical ecological functions these primates serve, such as dispersing seeds and promoting forest regeneration.
Habitat corridors offer an essential solution to combat these challenges by reconnecting isolated forest patches. These pathways enable howler monkeys to migrate freely, reducing the negative consequences of fragmentation and ensuring the health of forest ecosystems. Beyond safeguarding the survival of howler monkeys, these corridors yield cascading benefits: they support biodiversity, bolster forest resilience, and reinforce ecosystem stability on a broader scale.
In this exploration, we will assess the importance of habitat corridors for howler monkeys, examine the ecological and conservation implications of their implementation, and highlight actionable strategies to facilitate their effective design and deployment. These insights aim to guide policymakers, conservationists, and communities toward building a future where coexistence and ecological restoration thrive.
The Importance of Howler Monkey Habitat Corridors
Howler monkeys, famed for their resonant calls that carry across vast distances, perform vital roles in the health of tropical ecosystems. Unfortunately, their survival is increasingly jeopardized by habitat fragmentation caused by deforestation, agricultural expansion, and urban sprawl. These primates depend on expansive, connected forests with continuous canopy cover to access food, avoid predators, and travel between regions. The disruption of this connectivity creates isolated populations, leading to genetic bottlenecks, declining reproductive success, and an increased risk of localized extinction.
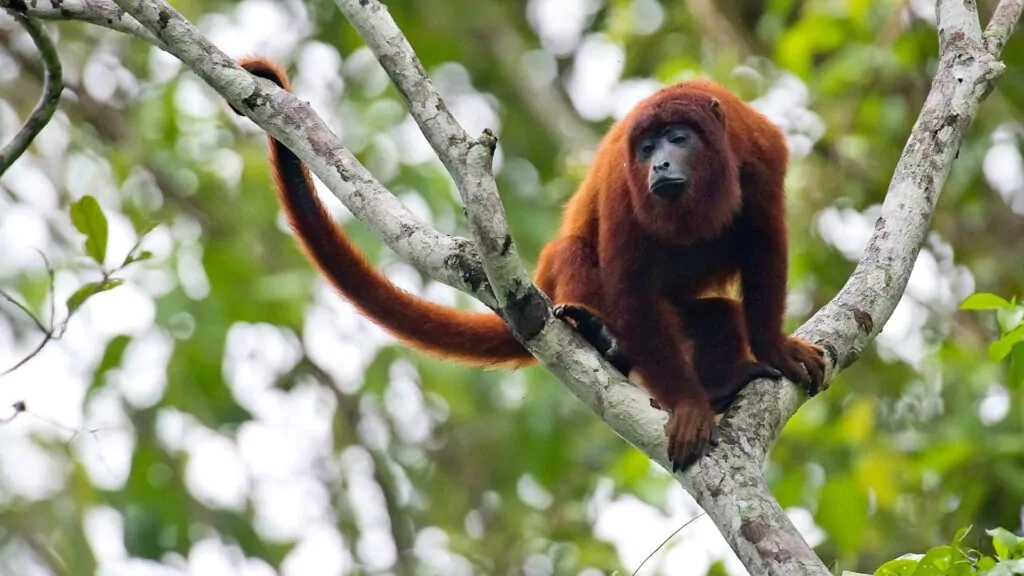
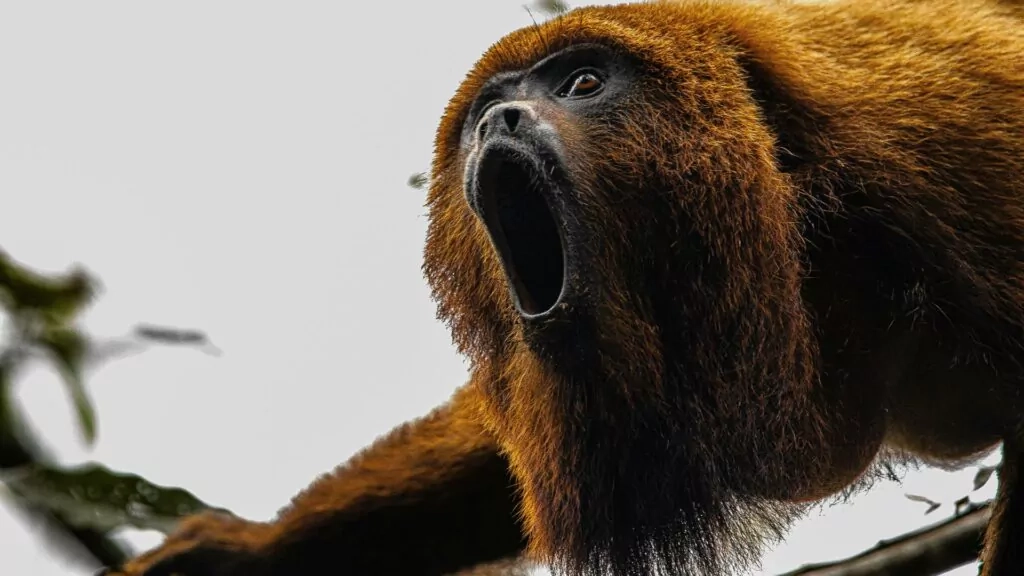


Importantly, habitat fragmentation undermines howler monkeys’ ecological contributions—most notably seed dispersal. By feeding on fruits and depositing seeds throughout their habitats, they promote forest regeneration and maintain biodiversity. However, fragmented landscapes restrict the primates’ range, confining them to smaller territories that cannot sustain viable populations or their critical roles in the ecosystem.
This is where habitat corridors come into play. These corridors reconnect fragmented landscapes, serving as “biological highways” that enable not just howler monkeys but a host of other species to move freely, access food and water sources, and maintain genetic health. Understanding how these corridors function and how to design them effectively is essential to reversing these adverse trends and preserving tropical biodiversity.
The Role of Habitat Corridors in Conservation
Habitat corridors are strategically designed passages that bridge fragmented landscapes, offering safe and navigable routes for wildlife. For howler monkeys, these corridors restore essential connectivity, granting them access to resources, shelter, and mates while expanding their habitable range.
How Habitat Corridors Enhance Genetic Connectivity
When howler monkey populations become isolated, they face heightened risks of inbreeding. This genetic isolation leads to diminished diversity, making populations more susceptible to disease and environmental pressures. Habitat corridors mitigate such risks by allowing primates to migrate between forest patches, encouraging genetic exchange and bolstering population resilience.


Supporting Ecological Functions through Connectivity
Beyond improving survival and genetic diversity, habitat corridors enable howler monkeys to fulfill their ecological responsibilities more effectively. As keystone species, these primates enhance biodiversity by dispersing seeds, even in degraded or deforested areas. In Mexico’s Los Tuxtlas region, research revealed that functional corridors increased both tree species diversity and density dispersed by black howler monkeys. These findings reinforce the dual benefits of corridors: they conserve individual species while simultaneously accelerating forest recovery and ecosystem regeneration.
By addressing both conservation and ecological imperatives, habitat corridors solidify their role as pivotal tools in biodiversity preservation and ecosystem management.
Key Considerations in Wildlife Corridor Design
For habitat corridors to succeed in safeguarding howler monkeys and other wildlife, they must be carefully planned with attention to ecological, social, and economic factors. Effective corridors should optimize wildlife movement while minimizing human-wildlife conflict and balancing the needs of local communities.
Design Principles for Effective Habitat Corridors
- Canopy Connectivity: As arboreal primates, howler monkeys rely on continuous tree canopy cover to navigate their environment safely. Corridors that lack sufficient canopy connectivity force monkeys to move on the ground, increasing their exposure to predators and roadway traffic. Ensuring an uninterrupted canopy is critical for their survival and movement.
- Width and Habitat Quality: Narrow corridors often expose wildlife to “edge effects,” such as greater susceptibility to predators and invasive plant species. Research suggests that corridors for primates like howler monkeys should ideally be over 100 meters wide to provide adequate protection and maintain viable habitat conditions.
- Location and Human Impact: Identifying strategic locations for corridors is essential to avoid proximity to high-traffic areas, agricultural zones, or industrial sites. Minimizing interaction with humans reduces stress and physical risks for howler monkeys and enhances the functionality of the corridors.
Integrating Shade-Grown Agriculture into Corridors
Innovative approaches like shade-grown agriculture offer promising solutions for multifunctional corridors. For instance, shade-grown cacao plantations can mimic natural forest habitats by preserving canopy cover while maintaining economic viability for farmers. Belize provides an excellent case study where such plantations have successfully linked fragmented forests, supporting black howler monkey populations while providing sustainable livelihoods for local farmers. This model underscores how well-integrated agriculture can align conservation goals with socioeconomic development.
By designing corridors that incorporate agroforestry and prioritize habitat quality, we can create landscapes that support both biodiversity and human prosperity.
Evidence-Based Insights on Corridor Effectiveness
The success of habitat corridors in restoring ecological balance and conserving species like howler monkeys is evident in several real-world examples.
In Colombia, efforts to connect forest fragments with biological corridors have led to tangible outcomes. Primate sightings along these newly established corridors increased by 32%, and genetic diversity improved significantly within 18 months. Camera traps and ecological monitoring provided compelling evidence of enhanced population activity, showcasing the effectiveness of systematic conservation efforts.

Notably, these projects generate economic dividends as well. Farmers engaged in conservation efforts often experience crop yield improvements due to enhanced pest control and pollination services fueled by enriched biodiversity. Such success stories underscore the manifold benefits of habitat corridors, which extend beyond environmental gains to deliver socioeconomic advantages.
Practical Strategies for Policymakers and Conservationists
Implementing habitat corridors successfully requires more than ecological expertise—it demands a multifaceted approach that includes robust policy frameworks, community engagement, and sustained financial investment. Policymakers and conservationists can drive large-scale progress by addressing these critical dimensions.
Actionable Steps for Effective Corridor Implementation
- Regional Connectivity Planning: Incorporate wildlife corridors into national and regional land-use plans. Creating zoning regulations that prioritize connectivity between forests, reserves, and buffer zones can help maintain continuous habitats for howler monkeys and other wildlife.
- Community Engagement and Incentives: Effective corridor implementation relies on local buy-in. Incentivizing landowners, a system perfected by Fund The Planet through eco-certifications to participate in conservation efforts which can encourage sustainable practices and improve corridor adoption in agricultural regions.
- Securing Global and Private Funding: International organizations such as the Global Environment Facility and private-sector partnerships can provide critical funding for corridor projects. Public-private collaborations often amplify conservation impact, merging large-scale financing with local implementation expertise.
Conclusion
Habitat corridors represent a cornerstone strategy in addressing the challenges of habitat fragmentation and safeguarding the survival of howler monkeys—critical keystone species essential to forest regeneration and biodiversity. By restoring connectivity, enhancing genetic diversity, and boosting seed dispersal, these corridors catalyze both species-specific conservation and broader ecosystem recovery.
Real-world examples, such as Costa Rica’s biological corridors and Belize’s agroforestry initiatives, highlight the effectiveness of integrating conservation goals with economic benefits. As policymakers, conservationists, and communities collaborate to scale these projects, habitat corridors emerge as a powerful model for balancing environmental sustainability with human prosperity.
Looking ahead, success in these efforts will depend on forward-thinking investments and widespread adoption of connectivity-centric land-use planning. By prioritizing the establishment of robust habitat corridors, we can ensure not only the survival of howler monkeys but also the continued vitality of the ecosystems upon which they—and humanity—depend.